If you have a passion for medicine and a desire to make a difference in people’s lives, becoming an anesthesiologist might be the perfect career path for you. This article will guide you through the steps you need to take to become an anesthesiologist, with a specific focus on students interested in pursuing this career in the USA. From completing undergraduate studies to medical school and residency training, we will explore the necessary educational requirements and provide valuable insights on what it takes to succeed in this rewarding field of medicine. So, let’s embark on this exciting journey together and discover the path to becoming an anesthesiologist.
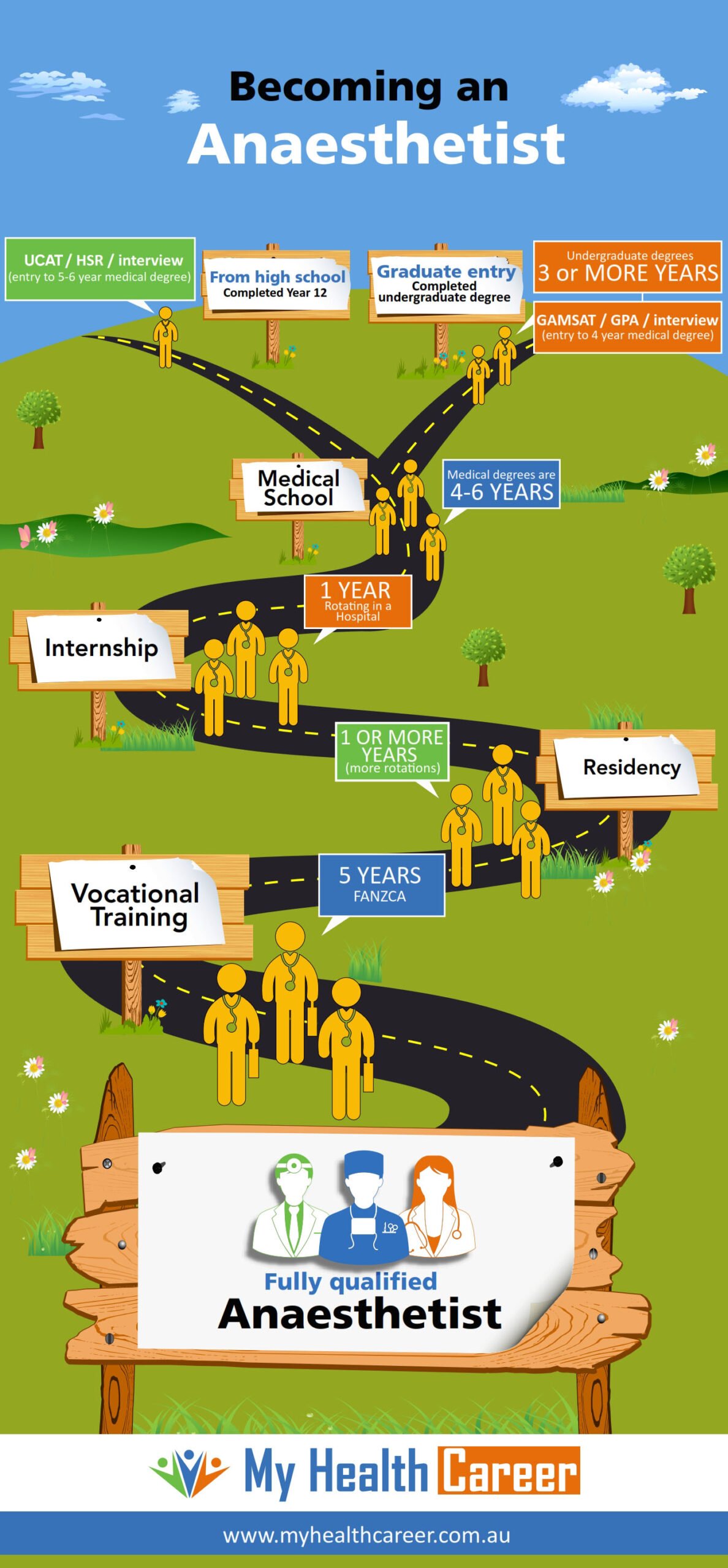
This image is property of www.myhealthcareer.com.au.
1. Obtain a Bachelor’s Degree
1.1 Choose a Pre-med Track
To become an anesthesiologist, the first step is to obtain a Bachelor’s Degree. As a student aspiring to pursue a career in anesthesiology, it is important to choose a pre-med track during your undergraduate studies. Pre-med programs are designed to provide you with the necessary foundation in basic science courses that are relevant to the field of medicine. These programs often include coursework in biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics, which are essential for medical school admission. It is advisable to consult with your academic advisor to ensure that you are selecting the appropriate courses for your chosen pre-med track.
1.2 Complete Prerequisite Courses
In addition to selecting a pre-med track, it is crucial to complete the prerequisite courses required for admission into medical school. The specific prerequisites may vary between medical schools, but generally include courses such as biology, chemistry (including organic and inorganic chemistry), physics, and mathematics. It is important to check the admission requirements of the medical schools you are interested in to ensure that you have completed all the necessary prerequisites. Taking these courses will help you build a strong foundation of knowledge in the sciences, which will be essential throughout your medical education.
1.3 Maintain a High GPA
Maintaining a high GPA is essential when pursuing a career in anesthesiology. Medical schools place a strong emphasis on academic performance, and a high GPA can greatly increase your chances of being accepted into a reputable medical program. It is important to prioritize your studies and strive for academic excellence in order to demonstrate your commitment and capability to succeed in the demanding field of medicine. In addition to your GPA, medical schools also consider other factors such as extracurricular activities, research experience, and letters of recommendation.
2. Take the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT)
2.1 Understand the Format and Content of the MCAT
The Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) is a standardized exam that is a requirement for admission into medical school. It is essential to familiarize yourself with the format and content of the MCAT in order to adequately prepare for this crucial exam. The MCAT assesses your knowledge and understanding in areas such as biology, chemistry, physics, psychology, and sociology. It also includes sections that evaluate your critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Understanding the structure of the MCAT will help you effectively plan your study strategy and allocate time to focus on the specific areas that require improvement.
2.2 Prepare for the Exam
Preparing for the MCAT requires careful planning and dedication. It is advisable to develop a study schedule that covers all the content areas tested on the exam and allows sufficient time for review and practice. There are various resources available to aid in your preparation, including MCAT review books, online practice questions, and study groups. Consider enrolling in a MCAT preparation course if you feel that you would benefit from structured guidance. Additionally, taking practice exams under timed conditions can help simulate the actual testing environment and improve your performance under pressure.
2.3 Register and Take the MCAT
Once you feel prepared and confident in your abilities, it is time to register for the MCAT. The MCAT is administered multiple times throughout the year, so you can choose a test date that suits your schedule. When registering, it is important to select a test center that is convenient for you and to allow ample time for studying and preparation leading up to the exam. On the day of the exam, it is essential to arrive early, well-rested, and equipped with all the necessary documents. Remember to bring valid identification and any required testing materials. Taking the MCAT is a significant step towards achieving your goal of becoming an anesthesiologist, so give it your best effort and remain focused throughout the exam.
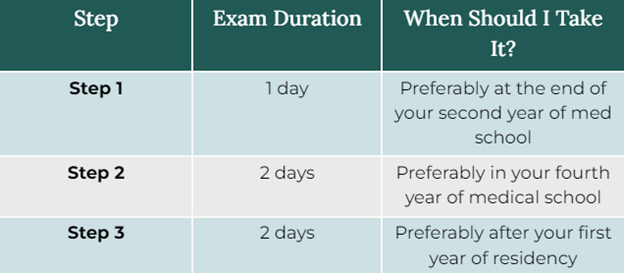
This image is property of uploads-ssl.webflow.com.
3. Apply to Medical School
3.1 Research and Choose Medical Schools
After successfully completing your undergraduate studies and the MCAT, the next step is to research and select the medical schools you wish to apply to. It is important to consider factors such as location, curriculum, reputation, and admission requirements when making your decision. Compile a list of medical schools that align with your educational and career goals, and take the time to thoroughly review their websites, admission criteria, and program details. This will help you make an informed decision and increase your chances of being accepted into a medical program that best suits your needs and aspirations.
3.2 Prepare Application Materials
The medical school application process can be complex and time-consuming, so it is important to start early and stay organized. Application materials typically include your personal statement, letters of recommendation, and a curriculum vitae (CV) or resume. Your personal statement provides an opportunity to showcase your passion for medicine and explain why you are interested in becoming an anesthesiologist. Letters of recommendation should be requested from professors, mentors, or healthcare professionals who can attest to your abilities and dedication. Your CV or resume should highlight your academic achievements, extracurricular activities, research experience, and any relevant healthcare or volunteer work.
3.3 Submit Applications through the American Medical College Application Service (AMCAS)
Most medical schools in the United States utilize the American Medical College Application Service (AMCAS) as the central application system. Therefore, it is essential to become familiar with the AMCAS application process and carefully follow the instructions. The application typically opens in May, and deadlines vary depending on the schools you are applying to. It is advisable to submit your application as early as possible to maximize your chances of being considered for admission. Be sure to review your application thoroughly for any errors or omissions before submitting it. Once your application is complete, it will be processed and transmitted to the medical schools you have selected.
4. Complete Medical School
4.1 Grasp Basic Medical Knowledge and Skills
Once accepted into medical school, you will embark on a rigorous and immersive educational journey. The first few years of medical school focus on building a strong foundation of medical knowledge and skills. You will attend lectures, participate in small group discussions, and engage in laboratory work to deepen your understanding of the human body, disease processes, and diagnostic techniques. The curriculum will also include courses in ethics, medical law, and patient communication, which are essential for providing compassionate and effective care as an anesthesiologist. It is important to approach your studies with dedication, discipline, and a thirst for knowledge in order to succeed in this demanding phase of your medical education.
4.2 Attend Clinical Rotations
In the latter part of medical school, you will have the opportunity to gain practical experience through clinical rotations. These rotations provide hands-on training in various specialties, including internal medicine, surgery, pediatrics, obstetrics and gynecology, and more. During your clinical rotations, you will work directly with attending physicians, residents, and other healthcare professionals to evaluate and manage patients. This is an invaluable experience that allows you to apply the knowledge and skills acquired during your preclinical years to real-world patient care. It is important to actively participate, ask questions, and seek opportunities to actively engage with different aspects of patient care, including anesthesiology.
4.3 Gain Exposure to Anesthesiology
While completing your clinical rotations, it is crucial to seek opportunities to gain exposure to the field of anesthesiology. This can be done by opting for anesthesia rotations or elective rotations in anesthesiology departments. By actively engaging with anesthesiologists and observing their work, you will gain firsthand insight into the practice of anesthesiology and the role of an anesthesiologist in patient care. This exposure will not only further solidify your interest in the field but also provide you with valuable experiences and connections that can be beneficial for your future career. Take advantage of every opportunity to learn and grow in the field of anesthesiology during your medical school journey.

This image is property of qph.cf2.quoracdn.net.
5. Pass the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE)
5.1 Understand the USMLE Steps
The United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) is a three-step examination series that assesses your knowledge and ability to apply medical concepts in a clinical setting. Each step of the USMLE is taken at different stages of your medical education and is essential for obtaining a medical license to practice medicine independently in the United States. Step 1 primarily tests your understanding of foundational science concepts, while Step 2 assesses your clinical knowledge and skills. Step 3 evaluates your ability to apply medical knowledge in the management of patient care. It is important to understand the format, content, and timing of each step in order to effectively prepare for and pass these examinations.
5.2 Study and Prepare for the Exam
Preparing for the USMLE requires diligent studying and disciplined practice. There are numerous resources available, including review books, question banks, online courses, and interactive study materials. It is advisable to develop a study plan that covers all the content areas tested in the USMLE and allocate sufficient time for review and practice. Consider creating a study group or seeking guidance from professionals who have successfully completed the USMLE. Regularly assess your progress with practice exams to identify areas that require further improvement. Remember to prioritize self-care during this challenging period and maintain a healthy work-life balance to prevent burnout.
5.3 Take and Pass the USMLE Step 1, 2, and 3
Once you have sufficiently prepared, it is time to take the USMLE Step 1, followed by Step 2 and Step 3. Each step is typically taken at different points during your medical education and training. It is important to register for each step in a timely manner and carefully follow the instructions provided by the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME). On the day of the examination, ensure that you arrive well-prepared, well-rested, and equipped with the necessary identification and testing materials. Taking and passing the USMLE is a significant milestone in your journey towards becoming an anesthesiologist, so approach each step with confidence and a strong foundation of medical knowledge.
6. Complete an Anesthesiology Residency Program
6.1 Research and Apply to Anesthesiology Residency Programs
After successfully completing medical school and passing the required licensing examinations, the next step is to apply for an anesthesiology residency program. Residency programs are typically three to four years in duration and provide specialized training in the field of anesthesiology. It is important to thoroughly research and identify the residency programs that align with your educational and career goals. Consider factors such as program reputation, faculty expertise, clinical experiences, research opportunities, and fellowship prospects when making your selection. Consult with mentors, attend informational sessions, and visit program websites to gather comprehensive information about each residency program of interest.
6.2 Gain Clinical Experience in Anesthesiology
During your residency program in anesthesiology, you will gain extensive clinical experience in the management of anesthesia for surgical procedures and other medical interventions. You will have the opportunity to work alongside experienced anesthesiologists, assist in the administration of anesthesia, and develop your technical skills. The residency program will also expose you to a wide range of subspecialties within anesthesiology, such as pediatric anesthesia, cardiac anesthesia, neuroanesthesia, and pain management. This exposure will allow you to explore different areas of interest and further refine your skills in specific subspecialties.
6.3 Complete the Accredited Residency Program
Completing an accredited anesthesiology residency program is a requirement for becoming an anesthesiologist. Throughout the residency program, you will undergo extensive training and evaluation to ensure that you acquire the necessary knowledge, skills, and clinical judgment required to practice anesthesiology independently. The program curriculum will typically include rotations in various subspecialties, didactic lectures, research opportunities, and hands-on clinical experiences. It is important to actively engage in your training, seek feedback from your supervisors, and take advantage of the resources and mentorship available to you. Successfully completing the residency program will position you for a successful career as an anesthesiologist.
This image is property of d92mrp7hetgfk.cloudfront.net.
7. Obtain Board Certification
7.1 Meeting the Requirements
Obtaining board certification in anesthesiology is an important step in solidifying your expertise and credibility as a healthcare professional. The specific requirements for board certification may vary, but generally include completion of an accredited residency program, successful completion of the required licensing examinations, and the demonstration of a certain number of clinical hours in anesthesiology. It is important to familiarize yourself with the specific requirements outlined by the American Board of Anesthesiology (ABA) or the relevant certifying body in your country.
7.2 Apply for Board Certification
Once you have met the requirements for board certification, the next step is to apply for certification through the appropriate certifying body. This typically involves submitting an application, paying the required fees, providing documentation of your training and clinical experience, and undergoing a thorough review process. It is crucial to carefully review the application instructions and ensure that all necessary documents are submitted accurately and within the specified timeframe.
7.3 Pass the Written and Oral Examinations
The final step in obtaining board certification in anesthesiology is to successfully pass the written and oral examinations. These examinations are designed to assess your knowledge, clinical reasoning, and ability to make critical decisions in the field of anesthesiology. The written examination evaluates your understanding of basic and clinical sciences related to anesthesiology, while the oral examination focuses on your practical application of knowledge and decision-making skills in patient care scenarios. It is important to dedicate sufficient time to prepare for these examinations, utilizing resources such as review books, practice questions, and mock oral exams. Passing the examinations will grant you board certification in anesthesiology and further enhance your professional standing in the field.
8. Consider Fellowship Training (Optional)
8.1 Explore Fellowship Opportunities
Upon completing your anesthesiology residency and obtaining board certification, you may choose to pursue further specialization by completing a fellowship in a specific area of anesthesiology. Fellowships offer additional, in-depth training in subspecialties such as pain medicine, critical care medicine, regional anesthesia, pediatric anesthesia, or obstetric anesthesia. Before selecting a fellowship, it is important to carefully research and explore various opportunities that align with your interests and career goals. Consider factors such as program reputation, faculty expertise, research opportunities, and the clinical exposure provided by each fellowship program.
8.2 Apply and Gain Acceptance
Once you have identified the fellowship(s) that interest you, the next step is to apply and gain acceptance into the program. The application process for fellowships is similar to the residency application process and typically involves submitting an application, letters of recommendation, a personal statement, and possibly participating in interviews. Be sure to thoroughly review the application requirements and allocate sufficient time to prepare and submit your application materials. It is important to highlight your previous training, clinical experiences, research endeavors, and future goals in your application to increase your chances of being accepted into the fellowship program of your choice.
8.3 Complete Fellowship Training
During your fellowship training, you will undergo specialized training and gain advanced knowledge and skills in your chosen subspecialty of anesthesiology. The duration of fellowships can vary depending on the specific program and subspecialty, ranging from one to three years. It is important to actively engage in your training, seek mentorship from experienced faculty, and take advantage of the research and clinical opportunities provided by the fellowship program. Successfully completing a fellowship will enhance your expertise and may open up new career opportunities in academia, research, or specialized clinical practice.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
9. Obtain a Medical License
9.1 Understand State-Specific Requirements
To independently practice medicine as an anesthesiologist, it is necessary to obtain a medical license in the state or jurisdiction where you intend to practice. It is important to understand the specific requirements and procedures for obtaining a medical license, as they can vary between states. Common requirements include completing an accredited medical education program, passing the required licensing examinations, providing documentation of your training and clinical experience, and passing a state-specific medical licensing examination or jurisprudence examination. Familiarize yourself with the licensing board of the state where you plan to practice to ensure that you meet all the necessary criteria.
9.2 Submit Application and Required Documents
Once you have met the state-specific requirements, you can begin the process of applying for a medical license. This typically involves submitting an application to the licensing board, along with the required supporting documents, such as transcripts, verification of training, licensing examination scores, and letters of recommendation. It is important to carefully review and complete the application forms, ensuring that all necessary information is provided accurately and in accordance with the instructions provided by the licensing board. The application process can be time-consuming, so it is advisable to start early and ensure that all required documents are obtained and submitted in a timely manner.
9.3 Pass the State Medical Licensing Examination
Many states require candidates to pass a state-specific medical licensing examination or jurisprudence examination as part of the licensure process. These examinations typically assess your knowledge of state laws, regulations, and ethical standards related to the practice of medicine. Thoroughly review the study materials provided by the licensing board and allocate sufficient time to prepare for the examination. Once you feel adequately prepared, schedule the examination and arrive well-rested and prepared to demonstrate your understanding of the state-specific requirements for medical practice. Passing the state medical licensing examination will grant you the medical license necessary to practice anesthesiology independently in that state.
10. Maintain Continuing Medical Education (CME) and Licensure
10.1 Fulfill CME Requirements
As an anesthesiologist, it is essential to stay up-to-date with advancements in medical knowledge, technologies, and practices. Continuing Medical Education (CME) is a requirement for maintaining your medical license and involves participating in educational activities that enhance your professional development. Each state has specific requirements for CME, including the number of hours or credits required per licensing period. Stay informed about the CME requirements of your state licensing board and proactively seek out opportunities to fulfill these requirements. Attend conferences, workshops, and seminars, and engage in self-directed learning to stay abreast of the latest research, guidelines, and best practices in anesthesiology.
10.2 Renew Medical License
Renewing your medical license is a recurring process that is typically required every few years, depending on the regulations of your state licensing board. It is important to remain vigilant regarding your license renewal dates and proactively submit the required documentation and fees within the specified timeframe. Failure to renew your license in a timely manner can result in suspension or revocation of your license. Keep track of the renewal requirements outlined by your state licensing board and ensure that you meet all the necessary criteria to maintain an active and valid medical license.
10.3 Stay Updated with Advancements in the Field
Anesthesiology is a rapidly evolving field, with advancements in techniques, technologies, and research occurring frequently. Therefore, it is essential to actively seek opportunities to stay updated with the latest developments in the field. This can be achieved through reading reputable medical journals, attending conferences and symposiums, and actively engaging in professional networks and associations. By staying informed and maintaining a continuous learning mindset, you can enhance your clinical skills, expand your knowledge base, and provide the highest standard of care to your patients.
Becoming an anesthesiologist is a challenging yet rewarding journey that requires dedication, perseverance, and a passion for medicine. By following these comprehensive steps and remaining committed to ongoing learning and professional growth, you can embark on a fulfilling career in the field of anesthesiology in the United States. Good luck on your path to becoming an anesthesiologist!